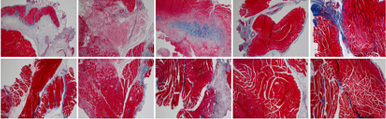
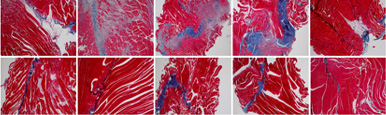
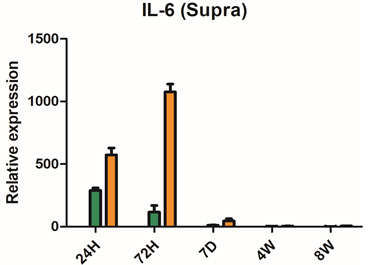
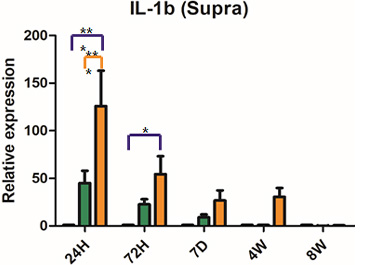
| Division | Division |
clinical
|
|---|---|---|
| Voiding Dysfunction | Interstitial Cystitis |
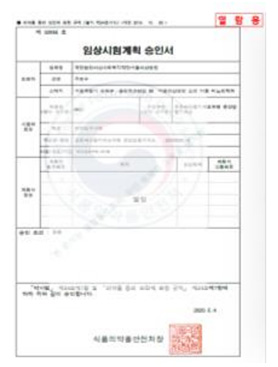
Orphan Drug Designation Approval
|
| Underactive Bladder(UB) | ||
| Overactive Bladder (OB) | ||
| Autoimmune Disorder | Atopic Dermatitis | |
| Urticaria | ||
| Musculoskeletal | Sports Injuries | |
| Neurological | Dementia |
| Division |
|
Notes |
|---|---|---|
| AD Pig | Development Complete, Mass Production | |
| Bio-derived Active Substances | Development and License Complete, Mass Production |
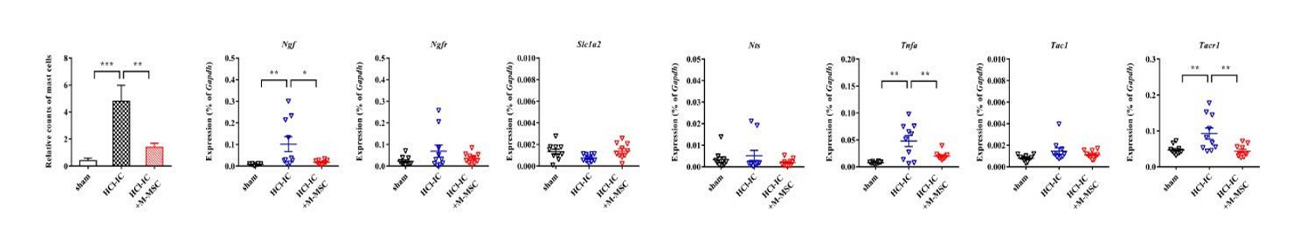
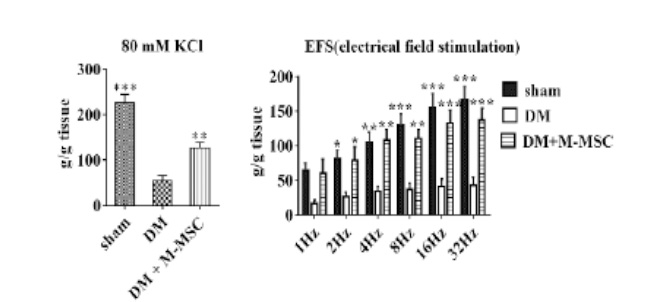
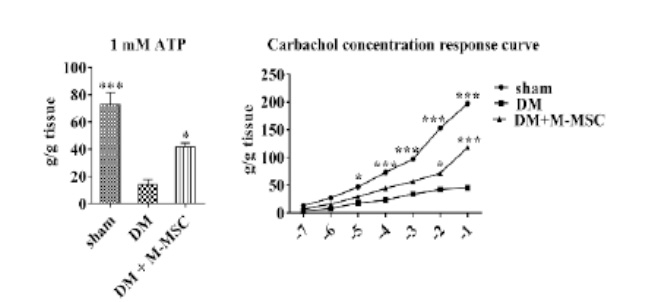
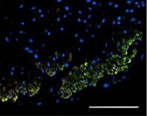
Severe inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology that causes bladder tissue damage with over 90% of the patients being female. According to Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Notice No. 30 published on November 12, 2020, this was designated as an orphan drug in the development stage.
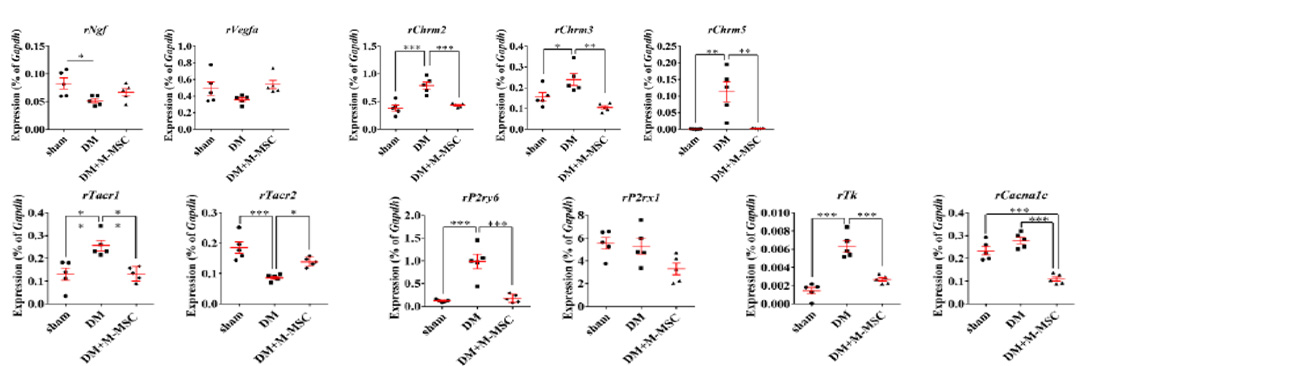
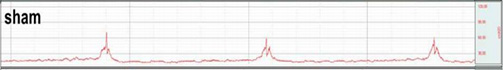
This is a disorder where urination does not happen even when the bladder is full due to the decreased function of the bladder muscles from aging or nerve damage. It is estimated that the number of patients will increase due to the aging population.
This is a disorder characterized by abnormal contraction of the detrusor muscle due to various reasons
causing incontinence regardless of the patient’s urge to urinate.
It has been evaluated that the number of sufferers of this disease is increasing especially
in the younger generation.
This is the most common degenerative brain disease that causes dementia. Cognitive dysfunction and behavioral disorders are caused by the apoptosis of brain cells, which is caused by the deposition of beta amyloids and phosphorylation of Tau proteins.
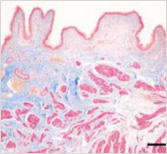
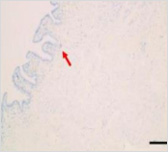
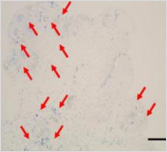
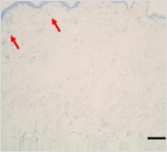
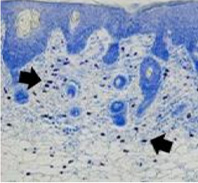
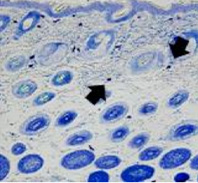
This is a skin disorder with various etiology and has been thought to be linked to the immune system. MMSC can decrease mast cells effectively, suppress immune reactions through immune regulation, and can be used in patients who do not respond to omalizumab and antihistamines.
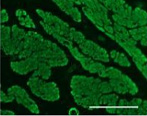
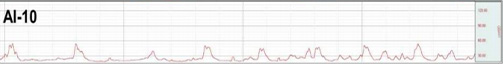
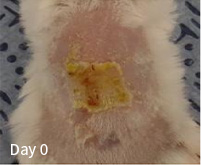
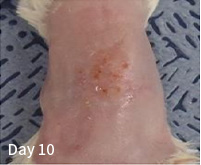
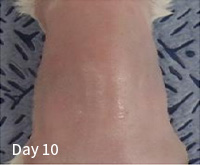
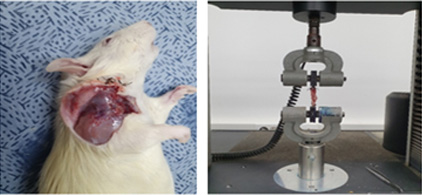
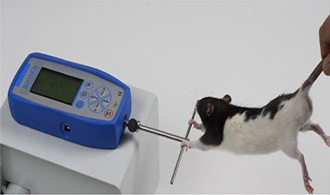
MMSC’s ability to suppress inflammation and promote tissue regeneration can greatly contribute to recovery from body tissue injuries. The efficacy of MMSC has been proven in rotator-cuff-tear animal models.